Air Sac Inflammation
Air Sac Inflammation
The most common form of air sac inflammation is caused by e.coli infection clinically. Symptoms of sick chickens include depression, difficulty breathing, abdominal respiration accompanied by snoring , coughing and tweeting. The air sac was found to be turbid by autopsy, with a large amount of turbid exudate,in severe cases,the air sac wall was thickened with cheese-like clots of varying sizes.
In addition to escherichia coli, H9 virus, new city disease virus, bronchitis, infectious bronchitis bacteria, infectious rhinitis virus, mycoplasma (septic mycoplasma, synovium mycoplasma, poison mycoplasma), aspergillus toxin and poor air circulation in the house, and high ammonia content, aggravates the occurrence of air sac inflammation in a way . There are 28 strains of mycoplasma alone, and different strains of mycoplasma have different sensitivity to drugs. In recent years, the main cause of the disease is H9N2 subtype avian influenza infection, and the pathogeny of air sac inflammation is very complex. If there is no clear target for clinical treatment, it is difficult to determine the pathogeny and choose effective drugs.
Air sac inflammation
major pathogenic factors
the temperature, humidity and ventilation do not meet the growth needs of chickens.
cardinal symptoms
coughing,sneezing,stretching the neck chirping, abdominal respiration accompanied by snoring
Disease analysis

The eyelids elongated and bubbles found at the corners of eyes
This disease is caused by mycoplasma septic infection secondary to escherichia coli infection,the secondary infection of Newcastle disease, avian influenza and infectious bronchitis in the middle and later stages affected by mycoplasma accounts for more than half of the incidence, and tht secondary infection can quickly cause the death of chickens. While those infected with non-virulent strains have no obvious clinical symptoms and cannot be easily detected, they will destroy the integrity of the mucosal barrier system of the respiratory tract and digestive tract, thus opening a door for the invasion of other pathogens. Finally a large number of chickens would die due to body autotoxicity caused by severe bacterial infection or due to a strong virus infection caused by physical weakness, which is the main reason for the failure of breeding.
Pathogenic factors

Being depressed,bowing and standing still
Improper control of ventilation, temperature, humidity and feeding density are the main inducing factors of air sac inflammation. In spring, autumn and winter, farmers always worry that the temperature of the chicken house is not high enough, so they do not often ventilate the chicken house, or in the case of inadequate ventilation facilities, it is easy to dry the air in the chicken house; The smoke and dust in the breeding house and the high density of feeding are likely to cause respiratory diseases; E. coli thrives in dry air; Mycoplasma gallisepticum can cause mixed infection of escherichia coli and air sac inflammation, at this point, the chicken's immunity decreases, leading to the occurrence of viral diseases.
Why does e. coli cause air sac inflammation?
Because the chicken has no diaphragm, its chest and abdominal cavity are separated by air sac, if the chicken digestive system be diseased, such as bacteria invasion, will soon cause the chicken respiratory system lesions, and then cause air sac inflammation.
Prevention and control measures:
Strictly carry out disinfection(water disinfection and chicken disinfection)
Select the best immunization method.( Immunization with lyophilized vaccine and oil vaccine)
Improve feeding management and ventilation conditions.( reduce feeding density, improve ventilation, avoid moldy feed)
Take symptomatic treatment for respiratory diseases .
Take aerosol therapy.
Actively cooperate with treatment (change the environment and repair mucous membrane when using medicine).
Clinical symptoms
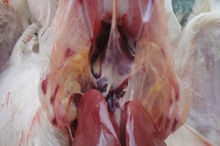
There are yellow inflammatory secretions in the thoracic air sacs
1.Chickens have mild respiratory symptoms at the beginning of the disease(snorting and shaking nose);the eyelids elongated and bubbles found at the corners of eyes; the Chickens’feed intake is basically not affected;the chicken droppings are dry ;no deaths occur.
2.In the middle of the disease,chickens would lower their heads,standing still with closed eys;they even have dyspnea,openinig their mouths,extending their necks,coughing and shaking their noses;the feed intake reduced and yellow-green loose stools would appear;the mortality rate reaches 0.2-1%.
3.If the chicken be sick for a long time,the comb will appear red and purple,and making strange cries sometimes. The sick chickens may experience depression, increased body temperature and the lack of appetite, and clustering or standing on one side;the feed intake of sick chickens would drop,and excreting white stools or yellowish green stools ,and the growth and development would become slow;some critically ill chickens would lie on the ground panting with their mouths slightly open.many of the dead chickens appeared to be in good condition,with inflammatory secretions blocking the bronchio found by autopsy.
4.Chickens that die from bronchial blockage caused by air sac inflammation are belly up.
Autopsy Results
1.there are needle-like bleeding points on larynx, cleft palate, eyelids;The trachea is bloodshot, bleeding and filled with mucus.
2.the chest air sac is turbid,thickened,with yellow or yellow-white inflammatory exudate,and there will be cheese-like attachments formed for the chickens that have been sick much longer.
3.Abdominal air sac is turbid, thickened, often with a large number of small air bubbles in the abdominal cavity (there is white mucous in the early stage), there will be cheese-like attachments formed for the chickens that have been sick much longer.
4.The anatomic symptoms of severely sick chickens are air sac inflammation, pneumonia, pericarditis, perihepatic inflammation, peritonitis, diffuse duodenal hemorrhage,Cecal tonsil enlargement and bleeding.
5.The bursa of fabricius is swollen or atrophied with purulent exudate, and the thymus is atrophied and bleeding.
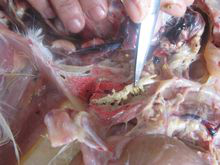
6.In severe cases, there is embolism in the lungs and bronchi.
Preventive measure
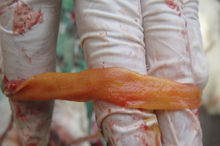
Diseased chickens have catarrh inflammation in their intestines
1.Increase the humidity , strengthen ventilation, reduce dust and improve the air quality in the house.
2.Kill mycoplasma, escherichia coli and salmonellosis when rearing chicks. At 15-19 days old, 22-27 days old and 31-33 days old,effectively carry out comprehensive prevention and control of bacteria and viruses.
3.Reduce stocking density; Once discovered the chicken group starts to get the respiratory tract disease,should adopt scientific and comprehensive drug treatment in time,because controlling respiratory tract and secondary infection in the shortest time is the key to prevent and cure this disease; but the hormone drugs are prohibited.
Solutions
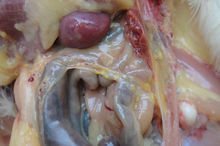
Cheese-like attachments on abdominal air sac
1.At the early stages
At this stage ,the typical upper respiratory symptoms are snoring,head shaking,sneezing,etc.no death at this time ,but if not treated well with drugs in time ,it is easy to lead to air sac inflammation and even death.At this time it is recommended to use “inhibitor”to treat ,dissolving 500g of “Inhibitor”in 750kg drinking water for chickens to drink , can effctively control respiratory symptoms and prevent the occurrence of balloon inflammation.
For exported poultry, it is recommended to use“Inhibitor” or“Qinangshukang” for treatment(each 500g of “Inhibitor”dissolved in 750kg drinking water for chickens to drink,or each 300g of “Qinangshukang”dissolved in 500kg drinking water ), which can effectively kill e. coli bacteria without drug residues.
2.In the middle of the disease
At this stage ,the respiratory symptoms of chicken group have worsened(the snoring becomes louder),and the lower respiratory tract has been infected and the diseased chickens begin to die.
At this time it is recommended to use “Qinangshukang”or “Rongshuantaimei”for treatment(each 300g of “Qinangshukang”dissolved in 500kg drinking water for chickens to drink,or each 500g of “Rongshuantaimei”dissolved in 1000kg drinking water ),once the treatment has been taken ,the occurance of continuous deaths of sick chickens can be effectively controlled within 48hours.
3.At the late stages
At this time the death rate is very high ,and it is very difficult to control the disease with a variety of drugs .it is recommended to use“Rongshuantaimei”for treatment(each 500g of “Rongshuantaimei”dissolved in 500kg drinking water).during 7-day withdrawal time, “Inhibitor”is available to use without drug residues(each 500g of “Inhibitor”dissolved in 750kg drinking water for chickens to drink).